How to Know If Your Child Has Allergies
Understanding Allergies in Children
Allergies are a common health issue affecting children of all ages. They occur when the immune system overreacts to certain substances, known as allergens, which are typically harmless to most people. Common allergens include pollen, dust mites, pet dander, certain foods, and more. When a child with allergies encounters an allergen, their immune system produces an allergic reaction, causing a range of symptoms.
Symptoms of allergies in children can vary depending on the type of allergen and the child's individual response. These symptoms may include sneezing, itching, a runny or stuffy nose, coughing, watery or itchy eyes, skin rashes or hives, wheezing or difficulty breathing, and gastrointestinal issues such as stomach pain, vomiting, or diarrhea.
Several factors can increase the risk of allergies in children. Genetics play a significant role, as children are more likely to develop allergies if one or both parents have them. Additionally, early exposure to certain allergens, such as through pet ownership or living in environments with high allergen levels, can contribute to the development of allergies. Other factors, such as a weakened immune system or early introduction of certain foods, may also increase the risk.
Identifying Allergy Triggers in Children
Understanding the common allergens that can trigger allergies in children, recognizing the signs to look out for, and implementing tips for minimizing exposure can help manage your child's allergies effectively. Common allergens include:
- Dust mites
- Pollen
- Mold spores
- Pet dander
- Food allergens such as peanuts, eggs, milk, soy, fish and seafood
These allergens can vary depending on the individual child, and it's essential to identify the specific triggers for your child's allergies. Look out for signs such as:
- Repeated sneezing or coughing
- Itchy or watery eyes
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Skin rashes or hives
- Difficulty breathing or wheezing
If you suspect that your child has allergies, consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and guidance.
Differentiating Allergies from Other Conditions
Allergies and colds can often have similar symptoms in children, making it difficult to determine the underlying cause. However, there are key differences between allergies and colds that can help you differentiate between the two.
Allergy symptoms tend to persist over a longer period of time compared to colds. Allergies can last for weeks or even months, while colds typically resolve within a week or two.
Another important distinction is the nature of the symptoms. Allergies often cause itching, such as itchy eyes, nose, or throat, which is not commonly associated with colds. On the other hand, colds usually come with a sore throat, congestion, and a runny or stuffy nose.
To determine if your child's symptoms are due to allergies, it's important to look for patterns. Allergies often occur seasonally or after exposure to certain triggers, such as pollen, dust mites, or pet dander. If your child's symptoms consistently appear during specific times or after exposure to certain allergens, it may be a strong indication of allergies.
While observing these patterns can be helpful, it is always recommended to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. A healthcare professional can conduct allergy tests, such as skin prick tests or blood tests, to identify specific allergens that may be causing your child's symptoms. This information can help guide appropriate treatment and management strategies.
Allergy Testing and Diagnosis
When your child experiences persistent symptoms such as sneezing, itching, or a runny nose, it's important to consider the possibility of allergies. Allergy testing can help identify the specific allergens causing these reactions, allowing for appropriate management and treatment.
There are several types of allergy tests available for children:
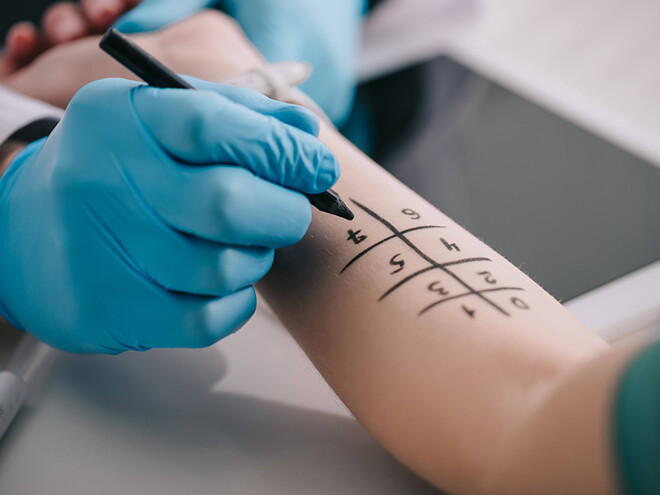
- Skin prick test: A small amount of allergen is applied to the skin, and any resulting reaction is observed.
- Blood test: A blood sample is taken to measure the level of specific antibodies (IgE) produced in response to allergens.
- Patch test: Small amounts of potential allergens are applied to patches that are placed on the skin to check for delayed allergic reactions.
Allergy testing is recommended when your child's symptoms are recurrent, unexplained, or affecting their daily life. It helps determine the substances triggering the allergies, which can include common allergens like pollen, dust mites, pet dander, certain foods, or medications.
The diagnostic process for allergies in children involves a comprehensive evaluation:
- Medical history: The healthcare provider will ask questions about your child's symptoms, their frequency, and any possible triggers.
- Physical examination: The doctor will assess your child's overall health and look for any visible signs of an allergic reaction.
- Allergy testing: Based on the medical history and examination, the healthcare provider may recommend specific allergy tests to identify the allergens causing your child's symptoms.
Once the allergens are identified, appropriate steps can be taken to manage and prevent allergic reactions. This may include avoiding the identified allergens, medication options, and developing an allergy action plan with your healthcare provider.
Managing and Treating Allergies in Children
Allergies in children can be a cause of concern for parents. It is important to effectively manage and treat allergy symptoms to ensure your child's well-being. Here are some strategies you can implement:
- Effective strategies for managing allergy symptoms: Identify the allergens that trigger your child's allergies and take steps to minimize their exposure. This may include keeping the house clean, using air purifiers, and avoiding outdoor activities during high pollen seasons. Additionally, ensuring a healthy diet and proper hydration can help strengthen your child's immune system.
- Medication options and their appropriate usage in children: Consult with your child's healthcare provider to determine the most suitable medication for their allergies. Antihistamines are commonly used to relieve symptoms such as sneezing and itching. Nasal sprays can help with congestion, and eye drops can alleviate itchy eyes. It is crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and instructions to avoid any adverse effects.
- Non-pharmacological approaches to alleviate allergy discomfort: In addition to medication, non-pharmacological approaches can also provide relief. Use hypoallergenic bedding and wash bedding frequently to minimize exposure to allergens. Keep windows closed to prevent pollen from entering the house. Saline nasal rinses can help clear nasal passages, and cool compresses can soothe itchy skin.
Preventing Allergies
Managing allergies may be difficult and may cause stress and worries to both the child and the caregivers. Note only does it cause modification in the lifestyle of the child and the family, it may also involve health care expenses starting from the detection procedures up to medications and treatments.
Allergies can be prevented, and parents can actively work towards reducing the risk of allergies and their associated complications by understanding and taking steps early. One of which is by understanding the role of genetics and environment on the risk of developing a child’s allergies even before it starts. [Link to Allergy Risk Tracker]
Let's take charge of our health by seeking reliable information, consulting with healthcare professionals, and implementing effective prevention strategies.